
- Mars can appear bright or faint in our sky. 2024 is mostly a faint year. Around February, Mars becomes visible in the east before dawn. It’s faint and far across the solar system from Earth.
- As the days pass, Mars will be climbing higher in the predawn sky, growing steadily brighter. Earth will be gaining on Mars, in our smaller, faster orbit around the sun.
- Around the September equinox, Mars will start becoming noticeable in our skies! By the year’s end, it’ll shine brightly at -1.2 magnitude. Its next opposition will come in January 2025.
Mars in 2024
Opposition for Mars last fell on December 8, 2022. That’s when our planet Earth last flew between Mars and the sun. It’ll reach opposition again in January 2025. Now, in February 2024, Mars will be ascending in the morning sky. In fact, Mars will be visible in the morning sky all year.
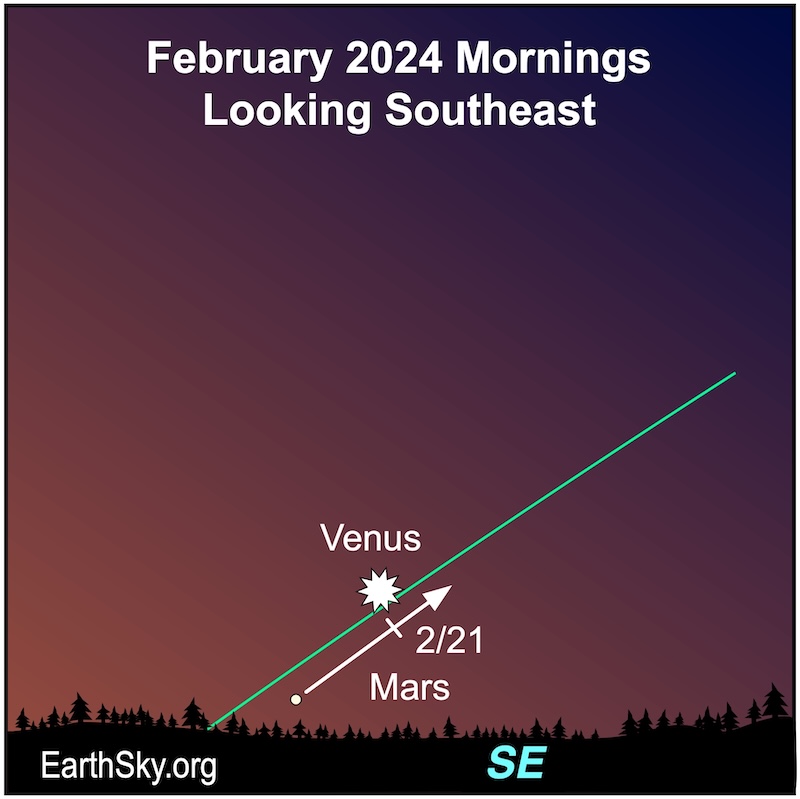
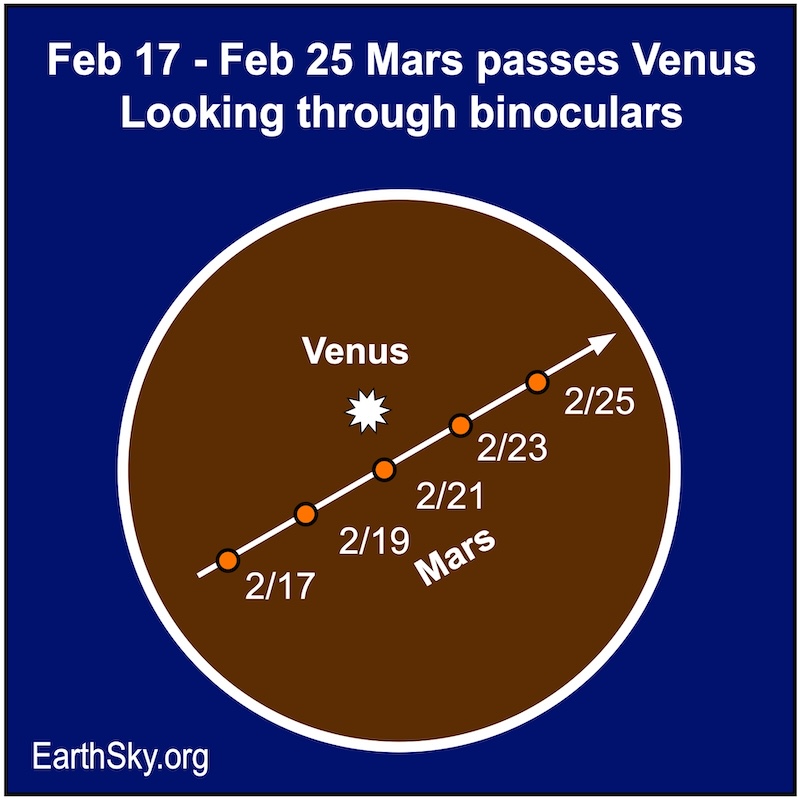
How to see Mars in the sky: In early February 2024, Mars will be low in the eastern morning sky and challenging to spot in the bright twilight. However, it’ll become easier to spot by month’s end. It’ll be shining at magnitude +1.3.
Constellations in February 2024: Mars, it would be crossing in front of the constellation Sagittarius and move in front of the constellation Capricornus the Sea-goat.
Note: Mars reaches opposition about every 26 months, or about every two Earth-years. So Mars alternates between appearing bright and faint in our sky. It was bright in late 2022 and early 2023. But by September 2023, Mars faded dramatically in brightness and disappeared in the sunset glare in October 2023. It passed behind the sun on November 18. It came back into view, in the east before sunrise, at the end of 2023 shining around magnitude +1.4.
Finder charts for February mornings

Sometimes, Mars is faint
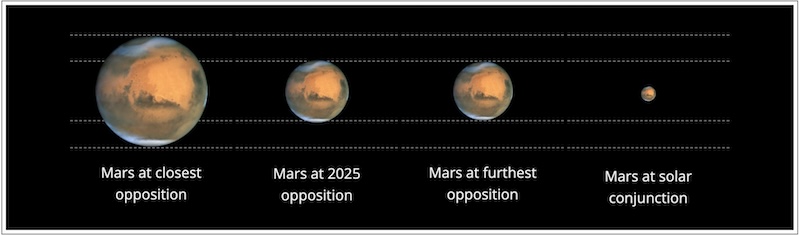
Mars was an inconspicuous faint red dot in the sky throughout the early months of 2022. It started becoming brighter in the final months of 2022 and reached opposition on December 8, 2022. It remained bright through early 2023, then started to rapidly fade through the end of the year. Mars reached superior conjunction on November 18, 2023. Now in 2024, it will remain faint until the last few months of the year.
Sometimes, Mars is bright
Mars steadily brightened in the first half of 2022, first as a morning object. But later, during the second half of 2022, Mars shone as a bright red ruby in the evening sky. Ultimately, it reached opposition – when Earth flew between Mars and the sun – on December 8, 2022.
Indeed, Mars’ dramatic swings in brightness (and its red color) are why the early stargazers named Mars for their God of War.
Sometimes the war god rests. And sometimes he grows fierce! In fact, these changes are part of the reason Mars is so fascinating to watch in the night sky.
Want to follow Mars? Bookmark EarthSky’s monthly night sky guide.
Mars isn’t very big
To understand why Mars varies so much in brightness in Earth’s sky, first realize that Mars isn’t a very big world. Indeed, it’s only 4,219 miles (6,790 km) in diameter, making it only slightly more than half Earth’s size (7,922 miles or 12,750 km in diameter).
On the other hand, consider Mars in contrast to Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is 86,881 miles (140,000 km) in diameter. As an illustration, more than 20 planets the size of Mars could be lined up side by side in front of Jupiter. Basically, Jupiter always looks bright, because it’s so big.
Not so for little Mars, however. Rather, its extremes in brightness have to do with its nearness (or lack of nearness) to Earth.

Future Martian oppositions
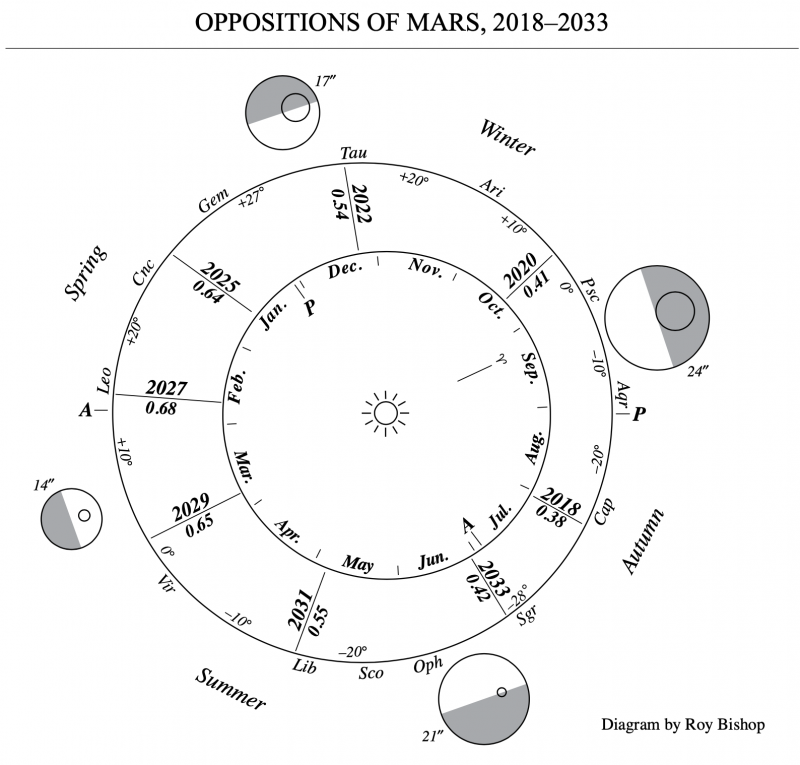
So, when is the next opposition of Mars? The next time Mars will appear at its brightest for that two-year period in our sky? You guessed it. In January 2025! Check out the chart on this page that lists all oppositions of Mars from 1995 to 2037.

Seeing red
Mars appears as a reddish light in the sky and, therefore, is often called the Red Planet. Other obvious red dots in the sky are reddish-orange Aldebaran and the famous red supergiant Betelgeuse. So, it is fun to compare Mars’ color and intensity of red with that of Aldebaran or Betelgeuse.
And then there is red Antares. Antares is Greek for rival of Ares, meaning rival of Mars. Antares is sometimes said to be the anti-Mars due to its competing red color. For a few months every couple of years Mars is much brighter than Antares. Also, every couple of years Mars passes near Antares, as if taunting the star. Mars moves rapidly through the heavens and Antares is fixed to the starry firmament.
What makes them red?
Surface temperature is what determines the colors of the stars. The hottest stars are blue and the coolest stars are red. In fact, from hottest to coolest, the colors of stars range from blue, white, yellow, orange and red. And while the colors of stars might be hard to detect, some stars – like Aldebaran, Antares and Betelgeuse – are noticeably colorful.
On the other hand, Mars appears red for a different reason. It’s red because of iron oxide in the dust that covers this desert world. Iron oxide gives rust and blood its red color. Rovers on Mars sampled the Martian dust and determined it contains three colors: reds, browns and oranges. So those three colors are what you may see when you gaze upon Mars.
Do you see red when you look at Mars, Aldebaran, Antares and Betelgeuse? Are they the same color? Do you see any other colors of stars?

Bottom line: Mars is back in our morning sky. In fact, it’s be visible in the morning sky for all of 2024 and it’ll reach opposition in January 2025.
Moon and Mars! Fav photos of December 7 occultation

