February 21 evening: Moon, Castor, Pollux, faint Beehive
On the evening of February 21, 2024, the bright waxing gibbous moon will shine near Castor and Pollux, the twin stars of Gemini. And it’ll be very close to the faint Beehive star cluster, which you likely won’t see in the moon’s glare, unless you’re an experienced stargazer. Ah, but when the moon moves away! In a dark sky, the Beehive is an easy target with binoculars. They’ll all rise before sunset and travel across the sky’s dome until a little before sunrise.

Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
February 17-25 mornings: Venus and Mars pair up
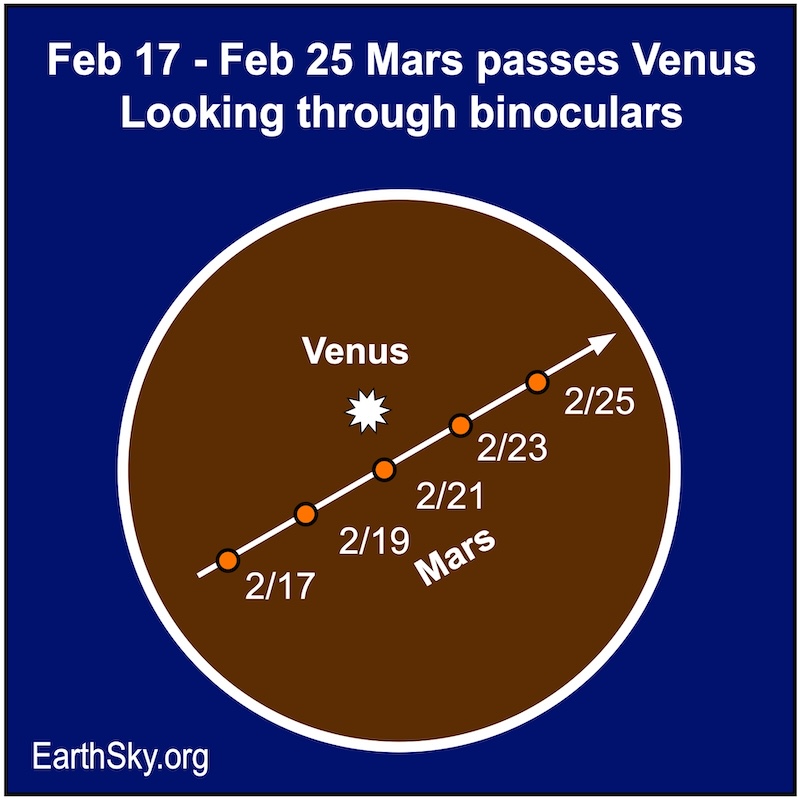
Here’s something worth getting up to see! Bright Venus pairs up with much-dimmer Mars from February 17 to 25, 2024. Mars is just now returning to our early morning sky after being behind the sun from Earth. It’ll be rising higher each morning, and it’ll pass brighter Venus, which is descending into the sunrise glare. So it’s a very bright object near a faint one! Fun to see. Mars and Venus will be closest to each other around February 21 and 22.
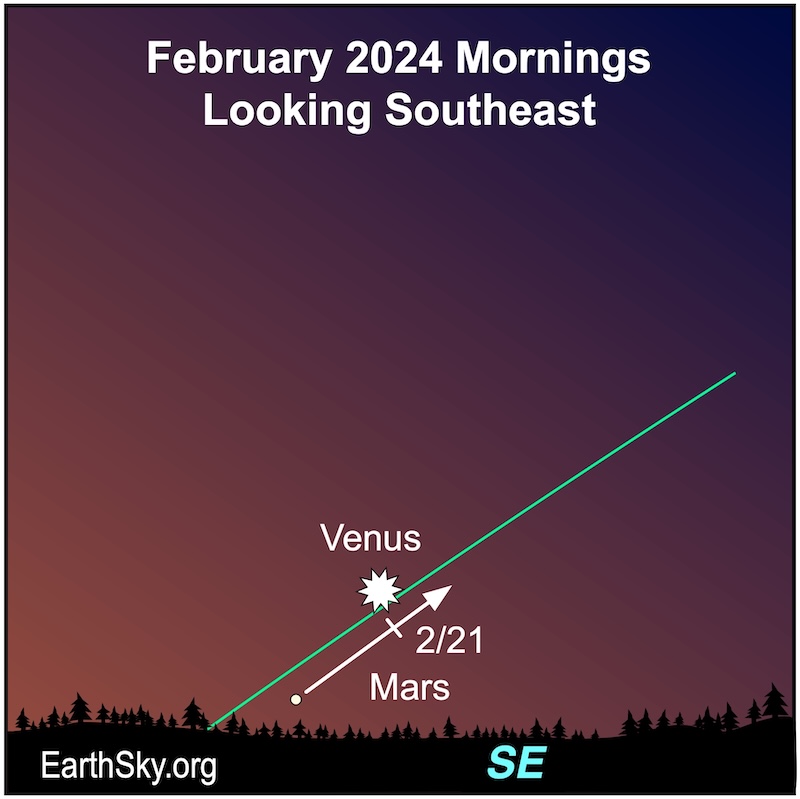
To enhance your view of Venus and Mars, use binoculars.
EarthSky Minute: Two morning planets
Solar eclipse countdown!
A total solar eclipse will cross North America on April 8, 2024. February 21, 2024, is 47 days until eclipse day. In this episode, Marcy Curran shares some fun facts of solar eclipses.
EarthSky Minute: February moon phases
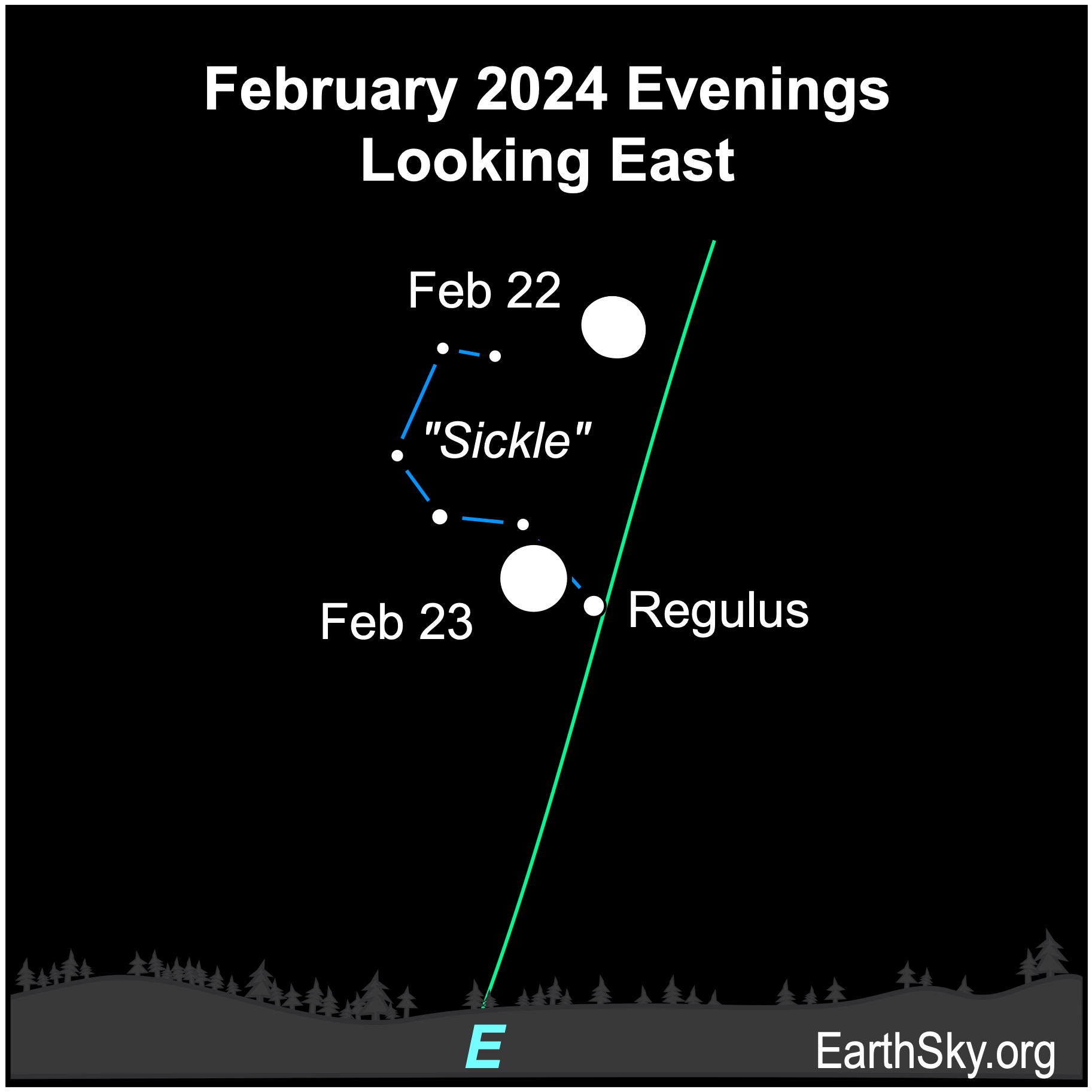
February 22 and 23 evenings: Moon near Regulus
On the evenings of February 22 and 23, 2024, the waxing gibbous moon will float near the star Regulus, marking the bottom of the backward question mark asterism called the Sickle. Regulus is the brightest star in Leo the Lion. They’ll be visible through dawn.
February 24, all night: Full Snow Moon
The instant of full moon – often called the Snow Moon – will fall at 12:30 UTC (6:30 a.m. CST) on February 24, 2024. But of course every full moon rises into your local sky around sunset … and sets around sunrise. This February full moon will be the smallest – most distant – full moon in 2024 at 252,225 miles (405,917 kilometers) away.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
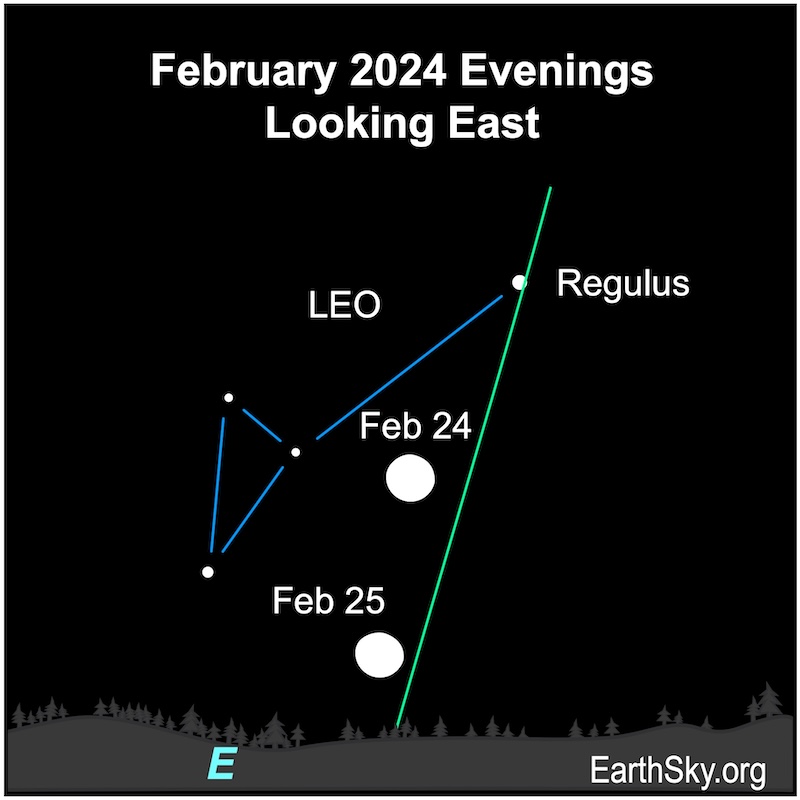
February 24 and 25 evenings: Moon near Regulus and Leo
On the evening of February 24, 2024, the full moon will pass the hindquarters of Leo the Lion. The waning gibbous moon will be approaching Leo on the evening of February 25. They’ll be visible all night.
Moon at apogee February 25
The moon will reach apogee – its farthest distance from Earth in its elliptical orbit around Earth – at 15 UTC (9 a.m. CST) on February 25, 2024, when it’s 252,470 miles (406,312 kilometers) away.
February 25 and 26 mornings: Moon near Regulus and Leo
On the mornings of February 25 and 26, 2024, the waning gibbous moon will lie near Regulus, the bright star marking the bottom of the backward question mark asterism called the Sickle. Regulus is the brightest star in Leo the Lion. They’ll rise the night before and be opposite the sun in the morning sky.

February 26 – March 11: Zodiacal light
The zodiacal light may be visible after evening twilight for Northern Hemisphere observers for the next two weeks. Southern Hemisphere observers? Look for it before morning twilight begins.
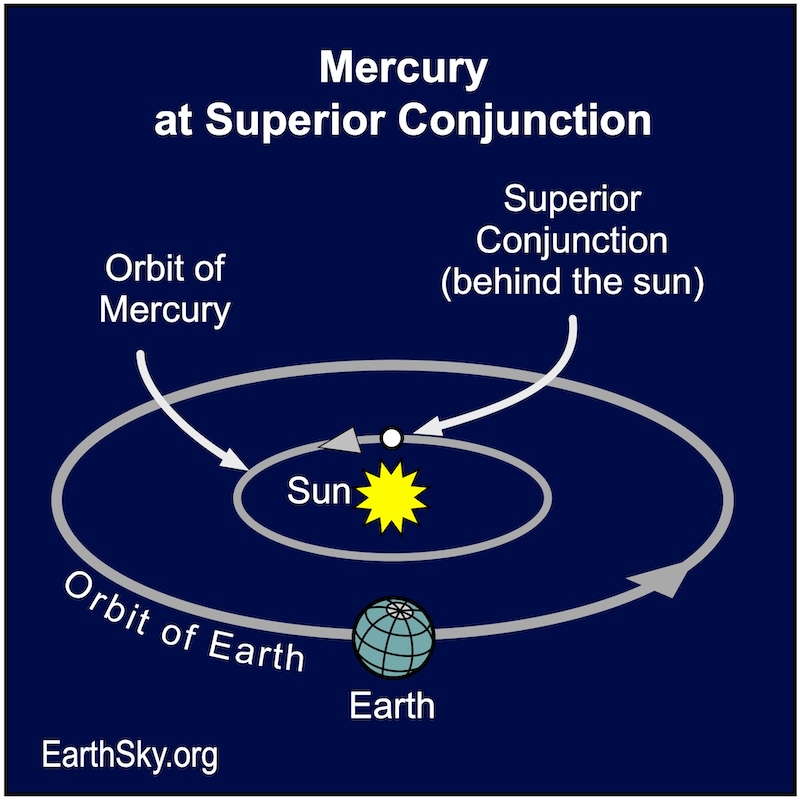
February 28: Mercury moves behind the sun
Mercury will move behind the sun on February 28. This point in its orbit is called superior conjunction. It will return to our evening sky in mid-March.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
February 28 and 29 mornings: Moon near Spica
On the mornings of February 28 and 29, 2024, the waning gibbous moon will hang near the bright star Spica in Virgo the Maiden.

Visible planets in February 2024
Mid-February mornings: Venus and Mars
In the middle of February, Mars will move close to brilliant Venus. They’ll be an interesting contrast in brightness, with Venus shining at magnitude -3.9 and Mars shining at +1.3. So Venus is roughly 100 times brighter than Mars. They will be at their closest on February 21 and 22, 2024. Then Venus will continue to descend closer to the sunrise each day, while Mars climbs out of the morning twilight.

Late February mornings: Venus and Mars
By the end of February, Venus will slowly be approaching the horizon before disappearing from the morning sky in March. And Mars will be climbing higher each day away from brilliant Venus. Mars remains a morning object through all of 2024.

February evenings: Jupiter
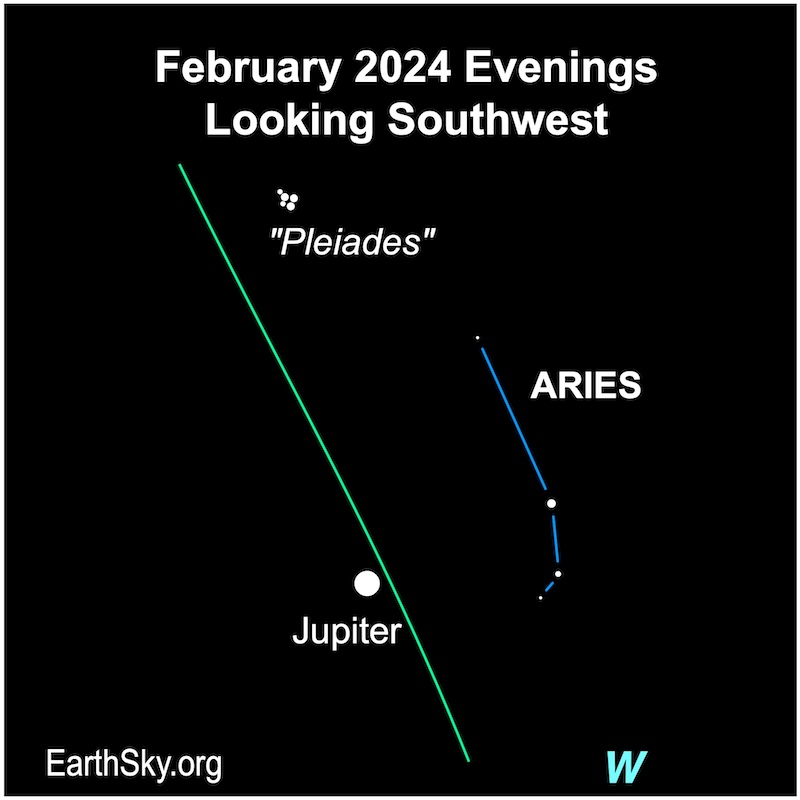
Bright Jupiter will draw your attention until around midnight in February 2024. It will be obvious high in the sky at sunset and will be visible until around midnight. It will shine near the pretty Pleiades star cluster in the constellation Taurus the Bull. Jupiter reached perihelion – or closest point to Earth – in early November. And it reached opposition overnight on November 2-3, 2023, when we flew between it and the sun. So, as Jupiter recedes from Earth, it’ll fade a bit in our sky. It will lie in the dim constellation Aries the Ram, and it’ll shine at -2.2 magnitude by month’s end. The 1st quarter moon will float by Jupiter on February 15, 2024.
Where’s Saturn?
Saturn will be in conjunction with the sun on February 28, 2024. It’ll emerge in the morning sky after mid-March.

Thank you to all who submit images to EarthSky Community Photos! View community photos here. We love you all. Submit your photo here.
Looking for a dark sky? Check out EarthSky’s Best Places to Stargaze.
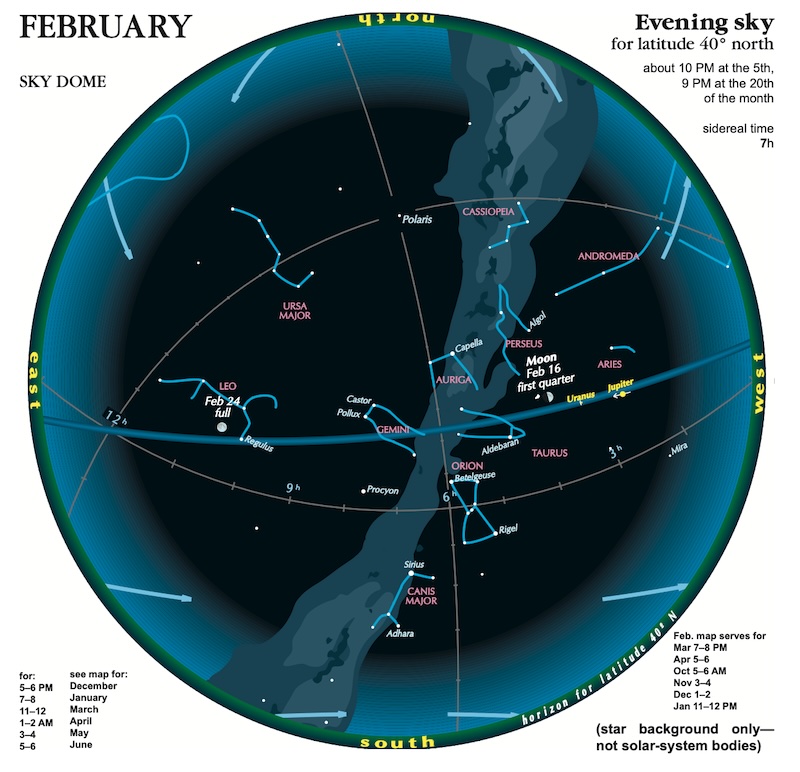
Sky dome maps for visible planets and night sky
The sky dome maps come from master astronomy chart-maker Guy Ottewell. You’ll find charts like these for every month of 2024 in his Astronomical Calendar.
Guy Ottewell explains sky dome maps
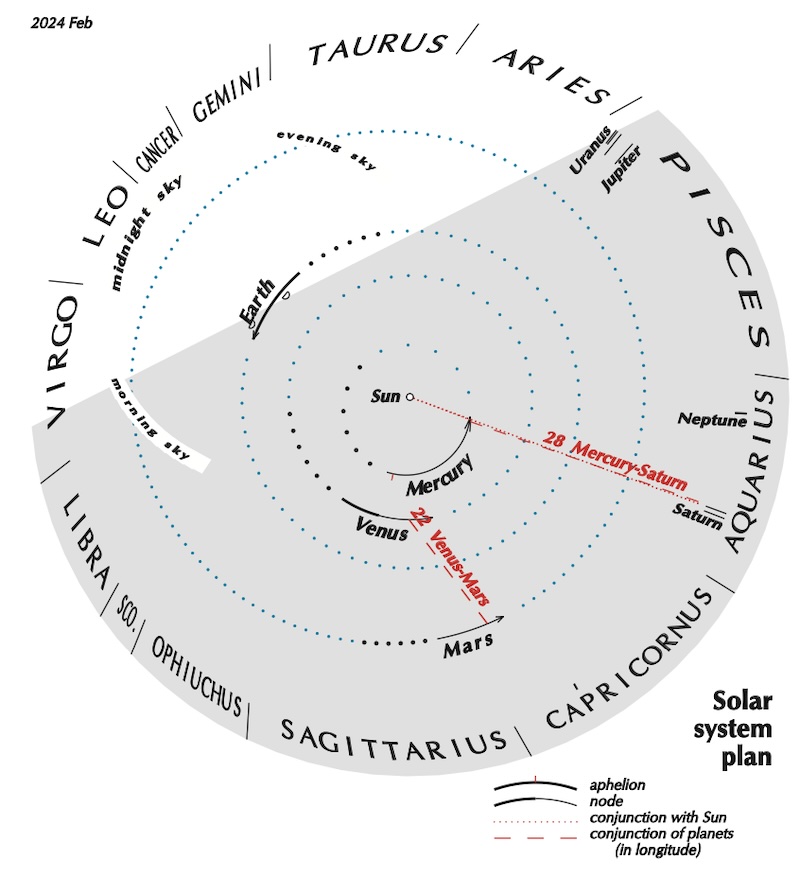
Heliocentric solar system visible planets and more
The sun-centered charts come from Guy Ottewell. You’ll find charts like these for every month of 2024 in his Astronomical Calendar.
Guy Ottewell explains heliocentric charts.
Some resources to enjoy
For more videos of great night sky events, visit EarthSky’s YouTube page.
Watch EarthSky’s video about Two Great Solar Eclipses Coming Up
Don’t miss anything. Subscribe to daily emails from EarthSky. It’s free!
Visit EarthSky’s Best Places to Stargaze to find a dark-sky location near you.
Post your own night sky photos at EarthSky Community Photos.
Translate Universal Time (UTC) to your time.
See the indispensable Observer’s Handbook, from the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada.
Visit Stellarium-Web.org for precise views from your location.
Almanac: Bright visible planets (rise and set times for your location).
Visit TheSkyLive for precise views from your location.

Bottom line: Visible planets in February. On February 21, we’re 47 days from eclipse day! See the moon, Castor, Pollux and the faint Beehive before sunset until a little before sunrise.

